설정에 따라 실제 외부 모듈과 통신하는 로직 테스트 해보기
들어가며
외부 모듈과 통신하는 로직 테스트는 외부 모듈이 제어할 수 없는 영역이므로 모킹 하여 외부 모듈에 대한 응답을 지정한 뒤 진행하기도 한다. 이때 외부 모듈이 실제로 기대한 응답을 내려줄 것이라는 것은 어떻게 테스트해 볼 수 있을까?
예를 들어 레디스에서 특정 키에 대해 특정 값을 응답할 것이라는 것을 모킹을 통해 응답 지정하여 로직을 테스트할 수는 있지만 실제로 특정 키에 대해 특정 값을 응답할 것이라는 것을 테스트해 보기 위해서는 레디스에 직접 요청을 해본 뒤 응답을 눈으로 확인해 본다거나 실제 레디스와 통신하는 테스트를 작성한 뒤 특정 키에 대해 예상하는 응답이 오는지 확인해 보는 방법이 있을 것 같다.
전자의 경우에는 외부 모듈마다 응답을 눈으로 확인하기 위한 방법이 모두 다르며 그런 방법이 복잡하고 번거로워진다면 테스트를 반복 수행하는데 한계가 있고 후자의 경우에는 테스트가 레디스 같은 외부 모듈에 강하게 종속되어 외부 모듈이 동작하지 않는 상황에서는 테스트가 실패할 수 있다는 단점이 있다.
기본적으로 외부 모듈과 통신하는 로직 테스트는 외부 모듈과 관계없이 테스트 가능하면서 원한다면 실제 외부 모듈이 동작하는 환경에서 테스트할 수 있는 방법을 알아보자.
외부 모듈과 관계없이 외부 모듈과 통신하는 로직테스트하기
어느 환경에서도 테스트를 수행했을 때 모두 통과할 수 있어야 한다고 생각한다. 즉 데이터베이스와 연결이 없어도 , 외부 서버가 동작하지 않아도 , 레디스와 연결이 되어 있지 않아도 모든 테스트는 통과해야 한다.
하지만 이는 쉬운 일은 아니다. 예를 들어 @Configuration 어노테이션이 붙은 RedisConfig 파일을 생성하여 레디스 설정을 진행하고 @SpringBootTest 어노테이션을 활용한 테스트를 진행한다면 RedisConfig 파일을 읽기 때문에 테스트 성공 여부가 레디스 실행 여부에 종속되게 된다. 즉, 레디스가 동작하지 않는다면 @SpringBootTest 테스트는 실패하게 된다. 이를 해결하기 위해서 @SpringBootTest를 사용하지 않는다거나 여러 가지 방법이 있지만 가장 쉬운 방법은 테스트 디렉터리에 같은 타입의 클래스 파일을 생성하는 방법이 있다.
main의 RedisConfig 파일이 com.XXX.XXX.global.config 위치에 있고 test의 RedisConfig 파일도
com.XXX.XXX.global.config 에 선언해 준다면 @SpringBootTest 시 test 의 RedisConfig 파일을 읽는다. test 의 RedisConfig 에서 레디스 실행 여부와 무관하게 설정해 준다면 더 이상 테스트의 성공 여부가 레디스 실행 여부에 종속되지 않게 할 수 있다.
외부 모듈과 관계없이 외부 모듈과 통신하는 로직을 테스트하기 위해서는 모킹 라이브러리를 활용하는 방법 이외에도 구조를 변경하는 방법도 있다.
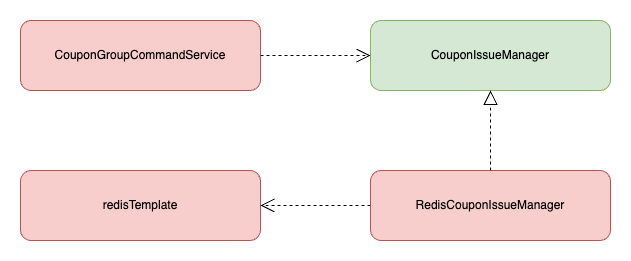
쿠폰 그룹 ID 를 key 값으로 발급 수량 value 을 레디스에 저장하는 요구사항이 있다고 했을 때 테스트 가능한 구조로 설계해 보자. 현재는 CouponGroupCommandService 가 레디스에 직접 의존하고 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public class CouponGroupCommandService {
private final CouponGroupepository couponGroupepository;
private final RedisTemplate<String, Integer> redisTemplate;
...
public Long create(final CouponGroupCreateRequest request, final int issueAmount) {
// request 로 쿠폰 그룹을 생성해준뒤 repository 에 저장한다.
CouponGroup couponGroup = couponGroupepository.save(request.toEntity());
// 쿠폰 그룹 ID 에 대한 발급 수량을 레디스에 저장한다.
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(couponGroupId, issueAmount);
return couponGroup.getId();
}
...
}
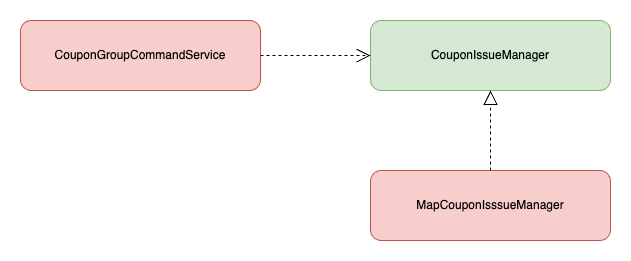
현재 구조에서 CouponGroupCommandService.create() 를 테스트하기 위해서는 모킹 라이브러리를 사용하거나 실제 레디스와 연동하는 방법 밖에 없다. 하지만 쿠폰 그룹 ID 에 대한 발급 수량을 저장하고 조회하는 기능을 추상화하고 동적으로 구현체를 주입할 수 있는 구조로 변경한다면 프로덕션 환경에서는 레디스 구현체를 등록하고 테스트 환경에서는 Fake 구현체를 등록하여 테스트할 수 있다.
코드는 다음과 같이 변경할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class CouponGroupCommandService {
private final CouponGroupepository couponGroupepository;
private final CouponIssueManager couponIssueManager;
...
public Long create(final CouponGroupCreateRequest request, final int issueAmount) {
// request 로 쿠폰 그룹을 생성해준뒤 repository 에 저장한다.
CouponGroup couponGroup = couponGroupepository.save(request.toEntity());
// 쿠폰 그룹 ID 에 대한 발급 수량을 couponIssueManager에 저장한다.
int issuedCouponAmount = couponIssueManager.issueCoupon(
persistCouponGroup.getId(),
issueAmount
);
return couponGroup.getId();
}
...
}
테스트 시에는 RedisConfig 파일을 다음과 같이 수정하여 RedisCouponIssueManager 를 주입받지 않고 MapCouponIssueManager 를 주입받아 테스트를 진행한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[test의 RedisConfig]
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public CouponIssueManager getCouponIssuer() {
return new MapCouponIssueManager(); // 테스트 용 CouponIssueManager
}
}
쿠폰 그룹 ID 로 발급 수량을 저장소에 저장하는 테스트는 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
@SpringBootTest
class CouponGroupCommandServiceTest {
@Autowired
private CouponGroupCommandService couponGroupCommandService;
@Autowired
private CouponGroupepository couponGroupepository;
@Autowired
private CouponIssueManager couponIssueManager;
@AfterEach
void tearDown() {
couponGroupepository.deleteAll();
couponIssueManager.clear();
}
@Test
@DisplayName("발급 수량 제한인 경우 쿠폰을 생성하고 발급 수량 만큼 쿠폰을 배포한다.")
void createAndIssue() {
int issueAmount = 1000;
CouponGroupCreateRequest request = getRequest(issueAmount);
Long couponGroupId = couponGroupCommandService.create(request);
assertThat(couponIssueManager.getIssuedCouponAmount(couponGroupId)).isEqualTo(issueAmount);
}
}
구조 변경 덕분에 동적으로 의존성을 주입 받을 수 있게 되었고 레디스 실행 환경과 설정과는 무관하게 테스트 가능하게 되었다.
이제부터 설정에 따라 실제 외부 모듈과 통신하는 로직을 테스트하는 방법에 대해 알아보자.
설정에 따라 실제 외부 모듈이 동작하는 환경에서 테스트하기
핵심은 @SpringBootTest 를 활용한 테스트를 실행할 때 MapCouponIssueManager 이 아닌RedisCouponIssueManager 를 주입하면 실제 레디스와 통신하는 로직을 테스트할 수 있다는 점이다.
test 하위의 RedisConfig 에서 프로퍼티 값에 따라 빈을 등록할 수 있는 @ConditionalOnProperty 를 사용하여 spring.redis.test=enable 일 때 레디스 관련 설정을 수행하도록 설정할 수 있다. 그리고 사용할 때@SpringBootTest(properties = "spring.redis.test=enable") 옵션을 주면 레디스와 관련된 빈이 등록되고 @Primary 어노테이션 통해 Fake 빈이 아닌 실제 빈을 주입하도록 한다면 실제 레디스와 통신하는 로직을 테스트할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
[test의 RedisConfig]
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
private final String host;
private final int port;
public RedisConfig(
@Value("${spring.redis.host}") final String host,
@Value("${spring.redis.port}") final int port
) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
@Bean
public CouponIssueManager getCouponIssuer() {
return new StubCouponIssueManager();
}
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.redis.test", havingValue = "enable")
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(host, port);
}
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.redis.test", havingValue = "enable")
@Bean
@Primary
public RedisTemplate<String, Integer> couponStore() {
RedisTemplate<String, Integer> couponStore = new RedisTemplate<>();
couponStore.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory());
couponStore.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
couponStore.setValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Integer.class));
return couponStore;
}
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.redis.test", havingValue = "enable")
@Bean
@Primary
public RedisCouponIssueManager redisCouponIssuer() {
return new RedisCouponIssueManager(couponStore());
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
@SpringBootTest(properties = "spring.redis.test=enable") // 레디스가 연결되어 있어야하며 실제 레디스와 통신하는 테스트이다.
class CouponGroupCommandServiceTest {
@Autowired
private CouponGroupCommandService couponGroupCommandService;
@Autowired
private CouponGroupepository couponGroupepository;
@Autowired
private CouponIssueManager couponIssueManager;
@AfterEach
void tearDown() {
couponGroupepository.deleteAll();
couponIssueManager.clear();
}
@Test
@DisplayName("발급 수량 제한인 경우 쿠폰을 생성하고 발급 수량 만큼 쿠폰을 배포한다.")
void createAndIssue() {
int issueAmount = 1000;
CouponGroupCreateRequest request = getRequest(issueAmount);
Long couponGroupId = couponGroupCommandService.create(request);
assertThat(couponIssueManager.getIssuedCouponAmount(couponGroupId)).isEqualTo(issueAmount);
}
}
마치며
모킹 라이브러리를 이용하여 외부 모듈과 통신하는 로직을 테스트하는 방법은 실제 외부 모듈과 통신하는 테스트를 진행하지 못하는 단점이 있다. 그래서 환경 및 설정에 따라 다른 빈을 주입할 수 있는 구조로 변경한 뒤 동적으로 의존성을 주입해 주면 실제 외부 모듈과 통신하는 테스트를 진행할 수 있다. 결국 실제 레디스와 통신하는 테스트를 진행해보고 싶다는 니즈와 레디스 실행 환경에 종속하지 않고 테스트할 수 있어야 한다는 니즈를 동시에 만족하기 위해 위와 같은 설정을 하였다. 주의할 점은 테스트를 진행하는 것이 외부 모듈에 영향과 다른 테스트에 영향을 주지 않도록해야한다는 점이다.